At this moment, the world’s most prominent researchers are dedicated to exploring the best treatment options for a variety of physical and mental health conditions. However, even with advancements in technology and understanding, there is still much we don’t understand about the human brain. For example, we know the brain is responsible for regulating all systems within the body, controlling the decisions we make, and for the internal and external responses to stimuli. Still, how the brain operates and controls these different systems still isn’t fully understood.
When individuals go to a medical professional to seek relief from a mental condition, such as anxiety, depression, or OCD, they are prescribed medication that is known to alter the way the brain functions. However, researchers still don’t understand how exactly this works. Today there is a better awareness of how dangerous it can be to continue to prescribe medication that alters the brain without fully realizing how and to what extent. This has pushed many medical professionals to consider alternatives to medications that can provide the same quality results. While many of these treatments still require extensive research over time, promising results have already been seen. One medical alternative to medication that continues to show promise is TMS therapy.
What Is TMS Therapy?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) improves symptoms of depression by stimulating nerve cells in the brain using magnetic fields. This therapy treatment is typically used as a repetitive treatment and can be referred to as rTMS. Unlike other therapies, this method is completely non-invasive. While this treatment is commonly considered when other treatments for depression don’t show desired effectiveness, its efficacy suggests that it may be a candidate to become a primary treatment.
TMS therapy is performed by placing an electromagnetic coil against the scalp near the forehead. A magnetic pulse is released painlessly, stimulating the nerve center of the brain. It is commonly believed that depression is a result of certain parts of the brain not being as active as they should.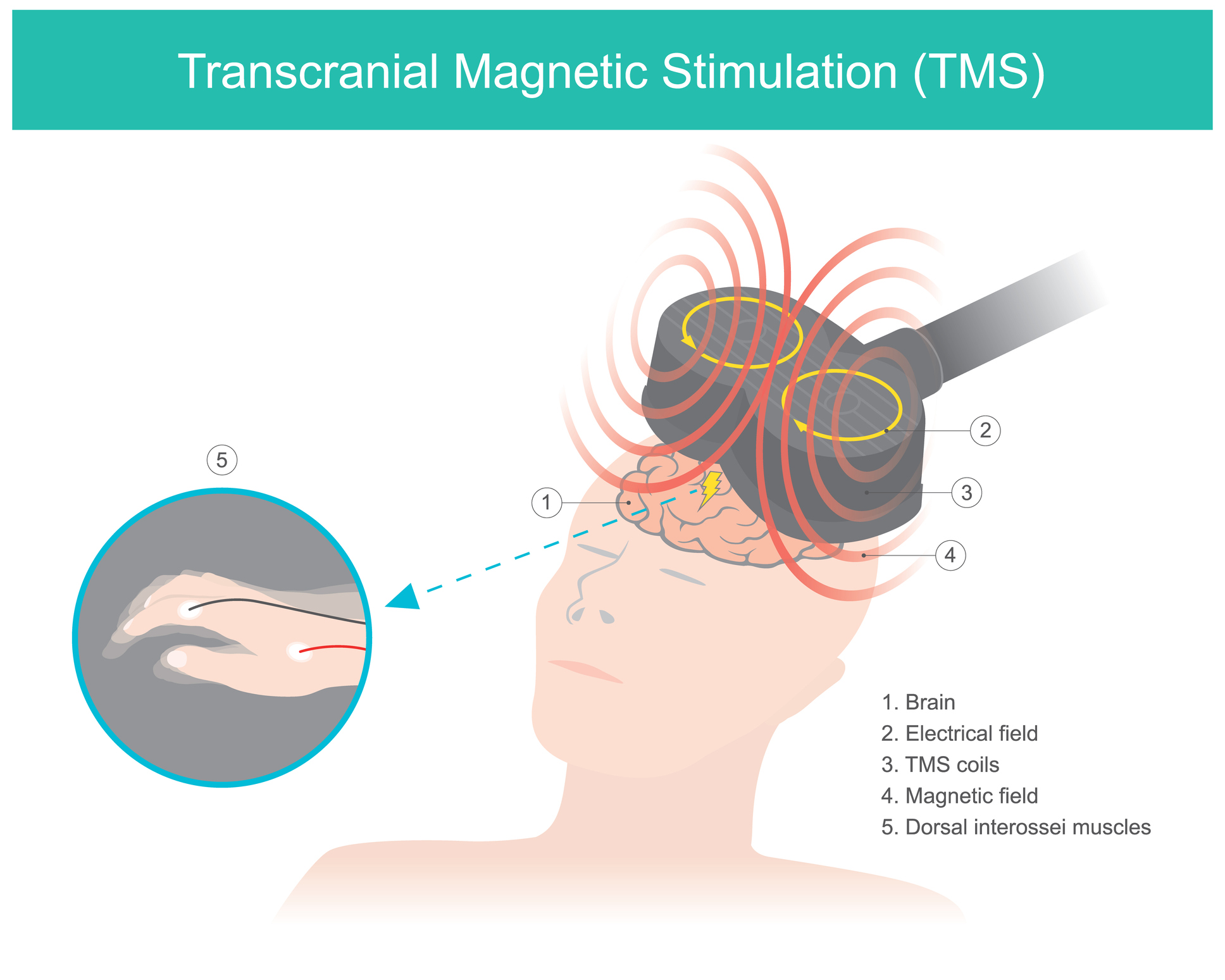
TMS therapy stimulates the underperforming areas of the brain, stimulating them to operate as they should. This can help to alleviate symptoms of depression. Targeting the part of the brain that is responsible for mood control can have positive medicinal benefits outside of depression alone.
TMS therapy needs to be applied on a consecutive basis for best results. This typically means attending therapy sessions five days a week for a prolonged period that can range from 6 to 8 weeks. These sessions typically last around 30 minutes. Since this method of therapy is non-invasive and doesn’t require sedation, an individual can easily go on with their day following their treatment session.
What Is TMS Therapy Used For?
TMS therapy has been FDA approved for the treatment of both depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).[fn]Cocchi, L., Zalesky, A., Nott, Z., Whybird, G. Fitzgerald, P. B., & Breakspear, M. (2018). Transcranial magnetic stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a focus on network mechanisms and state dependence. NeuroImage: Clinical, 19 , 661-674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.05.029 Research continues to explore other treatment options as well.
For example, experts are exploring the benefits of using TMS therapy to treat a variety of conditions such as:
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Attention-Deficit Disorder
- Hyperactivity Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Parkinson’s Disease
TMS and Addiction
Researchers are also continuing to explore the benefits of using TMS Therapy to treat addiction.[fn]Antonelli, M., Fattore, L., Sestito, L., Di Giuda, D., Diana, M., & Addolorato, G. (2021). Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: A review about its efficacy in the treatment of alcohol, tobacco, and cocaine addiction. Addictive Behaviors, 114, 106760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106760 Addiction is widespread, affecting a significant portion of our population, yet it is an issue still shrouded in misconceptions. Many still struggle to understand that addiction is a type of mental health condition that affects the brain.
There is a complex relationship between addiction and the brain, and addiction can affect the brain in a variety of ways.4 For example, addiction can overpower the brain’s attempts to satisfy any other needs, including basic care of the individual, such as eating, drinking, or sleeping. The brain can essentially lose control over the use of the addictive substance, prioritizing it above all else. Addictive substances can cause the brain to cease hindering its engagement in addictive behavior, regardless of the consequences. This is because drugs and alcohol directly affect the reward circuits of the brain that releases the neurotransmitter dopamine. This is meant to reinforce good behaviors that make us happy, but addiction can drastically warp this process.
There is a complex relationship between addiction and the brain, and addiction can affect the brain in a variety of ways.[fn]Koob, G. F., & Le Moal, M. (2008). Addiction and the brain antireward system. Annual Review of Psychology, 59(1), 29-53. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.59.103006.093548 For example, addiction can overpower the brain’s attempts to satisfy any other needs, including basic care of the individual, such as eating, drinking, or sleeping. The brain can essentially lose control over the use of the addictive substance, prioritizing it above all else. Addictive substances can cause the brain to cease hindering its engagement in addictive behavior, regardless of the consequences. This is because drugs and alcohol directly affect the reward circuits of the brain that releases the neurotransmitter dopamine. This is meant to reinforce good behaviors that make us happy, but addiction can drastically warp this process.
To overcome the effects addiction can have on the brain, providers rely on two primary means of treatment: counseling and medication. Counseling can include individual settings, group settings, rehabilitation centers, and other forms of treatment that focus on the way a person responds to their desire for their addiction, providing them with tools and methods for preventing thought patterns and decisions that can lead back to addiction. Medication is often used to help with withdrawal and relapse.

Withdrawal can be a serious concern for an individual trying to overcome addiction. Withdrawal symptoms can range from flu-like symptoms, fatigue, paranoia, seizures, strokes, and more, so medication is often used to offset the most severe of these. Since depression is a common symptom of withdrawal, many researchers are seeing promise in using TMS therapy to aid in the treatment of addiction. TMS therapy can help stimulate areas of the brain that may have been impacted by long-term drug or alcohol use. TMS therapy can also be a positive treatment option for individuals who would prefer not to rely on additional medications to aid in withdrawal symptoms.
Pros and Cons of TMS Therapy
There are a variety of pros and cons that are important to consider when determining if TMS therapy would be a good choice for your needs. Knowing what to expect can help you ask your medical provider specific questions, as well as give you a general idea of what to expect. Many individuals are turning to TMS therapy due to the numerous benefits.[fn]Carpenter, L. (2021). TMS Therapy: What Does the Future Hold? Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation, 14 (6), 1746.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2021.10.530
Pros
Non-Invasive
One of the best benefits of seeking TMS therapy is that it is the most non-invasive option for treating depression outside of talk therapy. TMS therapy is safer and less invasive than commonly prescribed anti-depressants. Anti-depressants can alter your neurotransmitters. They also come with a wide array of potentially dangerous side effects. For those who want a treatment option that is safe and non-invasive, TMS therapy is the best option.
Minimal Side-Effects
TMS therapy has little to no risk of side effects when done accurately. TMS therapy has no systemic side effects that are commonly associated with traditional medication used to provide depression treatment. TMS therapy doesn’t cause stomach issues, weight gain, dry mouth, or other side effects associated with antidepressant use.
Fits Your Routine
TMS therapy doesn’t require any sedation or medications, making it a great option for those with a busy schedule. Patients can maintain their daily schedule before and following their treatment. Patients can safely drive to and from their appointments.
Covered by Insurance
TMS therapy is growing in recognition when it comes to insurance providers understanding that it is a medical necessity for depression treatment. This is especially the case when other medications and therapies have failed. While TMS therapy is covered by many providers, there are still some restrictions that may have to be considered. Some providers won’t approve TMS therapy until two to four different antidepressants have proved unsuccessful. It is beneficial to know the detailed guidelines of your insurance provider.
TMS Therapy Is Effective
This method of treatment has shown its ability to provide effective, long-lasting results when it comes to treating depression and other disorders. Medically prescribed antidepressants have a rate of one in three when it comes to effectiveness. TMS therapy has a two in three rate, showing better results than traditional methods of treatment.

Non-Addictive
There is no risk of TMS treatment becoming addictive, as there is no habit-forming aspect of this treatment. This also means that there is no risk of withdrawal, which can be a common occurrence when trying to stop certain antidepressants.
No Memory Issues
There is a common misconception that treatments that directly involve the brain can present a serious risk when it comes to memory or cognitive ability. While ECT or shock therapy can run the risk of memory issues, this isn’t the case with TMS therapy. Research indicates that TMS therapy can enhance cognitive ability.
Cons
With any medical procedure, certain cons can be associated with the treatment. TMS therapy does have a variety of cons that should be considered when determining if this is the best treatment option for you.
Time Investment

TMS therapy is a repetitive method of treatment. This treatment can have sessions that last anywhere from 19-30 minutes. Sessions are usually spread over five days and can last for six weeks. This results in 30 treatments in total depending on the needs of the individual. While this adds up to less time typically recommended for seeking counseling, it can still be seen as an inconvenience for those with a busy schedule or if you have to travel for treatment.
Scalp Discomfort
Some patients experience mild scalp discomfort or headaches during or after treatment. This discomfort often goes away after a few treatment sessions.
Availability
TMS therapy treatment options are becoming more accessible as research continues to show the variety of benefits this treatment can provide. TMS therapy services can often be found in most major cities but may be more difficult to find in rural areas.
Potential Cost
While most insurance providers now offer coverage for TMS therapy, they can still enforce stipulations that dictate when they will cover this method of treatment. You’ll want to know your coverage options as well as your payment responsibility when it comes to any copay. If you are not covered by insurance, the cost of TMS treatment could be a serious hindrance.
TMS Therapy Side Effects
One of the best benefits of TMS therapy is that it has minimal side effects. The use of TMS to treat addiction is still fairly recent, leaving most information concerning side effects to focus more on short-term effects compared to long-term effects.
Common side effects are minimal, but could include:
- Headaches
- Tingling, spasms, or twitching
- Discomfort at the site of stimulation
- Light-headedness
Severe side effects are rare but can include seizures. Benign seizures can happen in 1 in 30,000 cases. Mania symptoms may increase in people with bipolar disorder. Hearing loss can also happen when proper ear protection is not worn.
Considering TMS Treatment
TMS treatment continues to show promise when it comes to safely stimulating areas of the brain that can be affected by depression, addiction, and other mental disorders. TMS treatment is a non-invasive, easy-to-conduct method of treatment. This treatment option is ideal for those who have tried other treatment options with no success. It is also beneficial for those who would prefer treatment methods that don’t rely on other medications that can ultimately be just as harmful. At Stairway Resource Center, we are dedicated to pursuing all methods of treatment that can help patients overcome their mental conditions and addictions. Contact us to learn more today.